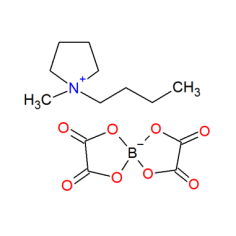
N-Butyl-N-methylpyrrolidinium Bis(oxalato)borate
- Brute formula
- C13H20NBO8
- CAS
- [625835-91-8]
- Molar mass
- 329.11

Ionic liquids or low-temperature molten salts represent a new class of solvents for a cleaner chemistry. Their low melting point, often below room temperature, offers significant energy savings. And unlike other solvents, they are infinitely recyclable.
Ionic liquids (also called room temperature molten salts or ionic solvents) are a new class of solvents offering interesting opportunities as a reaction medium for cleaner chemistry. Ionic liquids are salts comprising organic cations (for example imidazolium or pyridinium salts), complexed with inorganic or organic anions (such as, for example Cl-, Br-, AlCl4-, PF6- et BF4-, NO3-, (CF3SO2)2N-, etc.) which are liquid around room temperature.
General properties
Based on an innovative technology, ionic liquids are:
The physico chemical properties of ionic liquids depend on the type and the size of the two ions forming them. For example, ionic liquids containing chloride, bromide or trifluoroacetate anions are highly water soluble (hydrophilic). Conversely, when they are associated with an anion such as hexafluorophosphate or bis(trifluoromethanesulfonyl)imide, water solubility is very limited (hydrophobic), forming two liquid phases.
Advantages
It's possible to design tailor-made ionic liquids by adjusting the cation/anion combination or modifying their structure, offering properties suited to a wide range of applications. For more information and to discuss your specific needs, contact us now !
